Microemulsions are a fascinating aspect of scientific exploration that lie at the intersection of chemistry, physics, and material science. These unique systems have captivated researchers and industries alike due to their exceptional stability and versatile applications. This comprehensive article serves as an invaluable source of knowledge, delving into the intricate scientific principles that unveil the mysteries behind microemulsion.
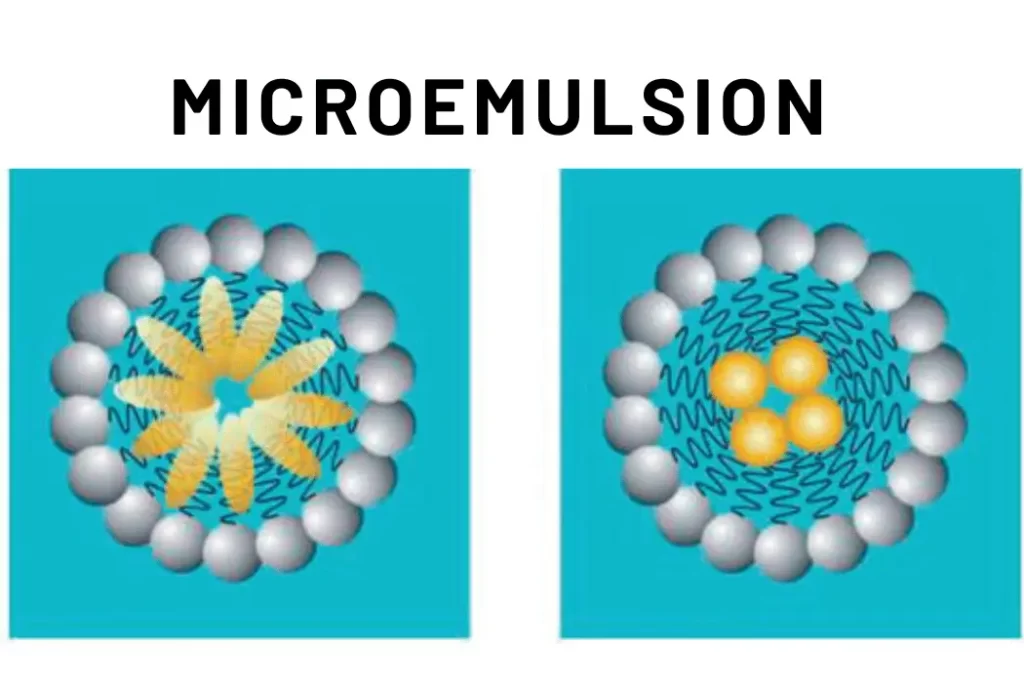
Microemulsion, colloidal systems composed of water, oil, surfactants, and sometimes co-surfactants, have garnered immense scientific interest. These systems are characterized by their thermodynamic stability and transparent appearance, often resembling clear solutions. In microemulsion, small droplets of one liquid are dispersed in another through the aid of surfactants, which lower the interfacial tension between the two phases, allowing them to mix homogeneously.
Components and Phases
Microemulsion consist of three main components: water, oil, and surfactants. Depending on the system, a co-surfactant might also be present. These components self-assemble into different phases: oil-in-water (O/W), water-in-oil (W/O), and bicontinuous. The unique aspect of microemulsion is their ability to spontaneously form and maintain their stability due to the intricate balance of forces at play.
Thermodynamics of Formation
The formation of microemulsion is driven by thermodynamics. As the components try to minimize their free energy, they organize themselves to achieve the most stable configuration. The amphiphilic nature of surfactants enables them to arrange at the oil-water interface, preventing droplet coalescence and maintaining a uniform dispersion.

Factors Influencing Microemulsion Formation
Surfactants and Emulsifiers
Surfactants play a pivotal role in microemulsion formation. They possess both hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments, allowing them to align at the oil-water interface and stabilize the system. Emulsifiers aid in reducing interfacial tension, enabling the mixture of immiscible liquids.
Temperature and Pressure
Temperature and pressure significantly influence microemulsion formation. Changing these parameters can lead to phase transitions or even phase separation. The delicate balance between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic components can be disrupted under extreme conditions, affecting stability.
Composition and Salinity
The proportion of water, oil, and surfactants, along with the presence of co-surfactants, determines the microemulsion’s properties. Salinity can impact the system’s behavior, with ionic interactions affecting the arrangement of molecules at the interface.
Characteristics of Microemulsion
Particle Size and Structure
Microemulsions are known for their incredibly small droplet sizes, typically ranging from 10 to 100 nanometers. This small size contributes to their optical transparency and stability. The droplets’ uniform distribution gives microemulsion their characteristic clarity.
Optical Transparency
Microemulsion exhibit optical transparency due to the small droplet sizes and their homogeneous distribution. This property makes them suitable for various applications, including transparent formulations in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Stability and Phase Behavior
The thermodynamic stability of microemulsion is due to the surfactant molecules forming a protective layer around the droplets, preventing them from coalescing. This stability is a result of the balance between attractive and repulsive forces at the interface.
Applications Across Industries
Microemulsions have found applications across diverse industries due to their unique properties and stability.
Pharmaceutical and Drug Delivery
Microemulsions are employed in pharmaceuticals for enhancing the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs and improving their bioavailability. Their small droplet sizes facilitate rapid absorption in the body.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
The optical transparency and ease of formulation make microemulsion popular in cosmetics. They are used in skincare products, sunscreens, and hair care formulations.
Enhanced Oil Recovery
In the oil industry, microemulsion aid in enhanced oil recovery by improving the displacement of oil from reservoirs. They can solubilize and mobilize oil, leading to increased extraction efficiency.
Food and Beverage
Microemulsion find applications in the food and beverage industry for encapsulating flavors, vitamins, and bioactive compounds. They improve the stability and delivery of these components in various products.
The Science Behind Stability
Gibbs-Thomson Effect
The Gibbs-Thomson effect explains the relationship between droplet size and curvature. Smaller droplets have higher curvature, leading to increased pressure within them. This pressure difference affects the droplet stability.
Ostwald Ripening
Ostwald ripening is a phenomenon where larger droplets grow at the expense of smaller ones due to differences in solubility and surface energy. This process can lead to instability in microemulsion over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Microemulsion
Microemulsion offer several advantages, including improved drug delivery, enhanced stability of ingredients, and the ability to encapsulate hydrophobic compounds. Their versatility makes them suitable for various applications.
Disadvantages of Microemulsion
Despite their numerous benefits, microemulsions also have limitations. They can be challenging to formulate due to the sensitivity of their stability to changes in composition and environmental factors.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Tailoring Microemulsion for Specific Applications
As researchers deepen their understanding of microemulsion behavior, they can tailor these systems to suit specific applications. Customized microemulsion could revolutionize industries like medicine and cosmetics.
Incorporating Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology holds the potential to further enhance microemulsion properties. By incorporating nanoparticles into these systems, researchers can create hybrid materials with novel functionalities.
Environmental and Sustainable Applications
Exploring environmentally friendly surfactants and optimizing microemulsion processes could lead to more sustainable applications in fields like agriculture and pollution control.
Conclusion
Microemulsion stand as remarkable examples of how intricate scientific principles can be harnessed for practical applications. Their stability, transparency, and versatility make them invaluable assets in various industries. As research continues to unveil the science behind microemulsion, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Are microemulsions the same as regular emulsions?
Answer: No, microemulsions have much smaller droplet sizes and unique stability compared to conventional emulsions.
Q2: Can microemulsion be used in food preservation?
Answer: Yes, microemulsions can encapsulate preservatives and improve their delivery in food products.
Q3: What role do surfactants play in microemulsion formation?
Answer: Surfactants lower the interfacial tension between oil and water, enabling the formation of stable microemulsions.
Q4: How are microemulsions relevant to the energy sector?
Answer: Microemulsions aid in enhanced oil recovery, contributing to more efficient oil extraction.