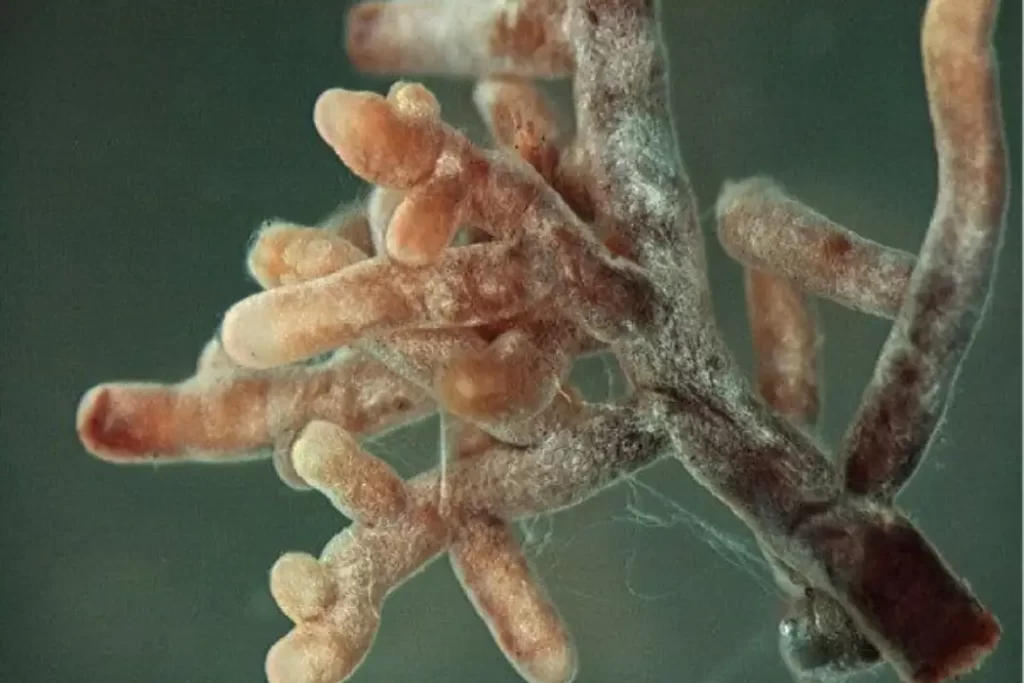
Soil is teeming with microscopic life, and among the many fascinating organisms that inhabit it, actinomycetes hold a special place. These versatile bacteria play a crucial role in soil microbiology, contributing to the overall health and fertility of the soil. In this article, we will delve into the world of actinomycetes, exploring their characteristics, functions, and the importance of their presence in soil ecosystems.
Actinomycetes are a group of bacteria that share characteristics of both fungi and bacteria, making them unique in the microbial world. Actinomycetes, the hidden heroes of soil microbiology, are not only essential for soil health but also serve as a valuable source of knowledge in understanding the intricate workings of microbial ecosystems. They are gram-positive, filamentous bacteria with a high G+C content in their DNA. Actinomycetes are commonly found in soil, but they can also be present in aquatic environments, compost, and even in the gut of animals.
Characteristics of Actinomycetes
Actinomycetes are characterized by their filamentous growth pattern, which forms branching networks called mycelia. These mycelial structures enable actinomycetes to access and explore different niches in the soil, contributing to their ecological versatility. Actinomycetes produce spores as a means of reproduction, allowing them to survive unfavorable conditions and disperse to new environments.
Diversity and Distribution
Actinomycetes are an incredibly diverse group of bacteria, with over 2,000 known species. They belong to the phylum Actinobacteria, which also includes other important genera such as Streptomyces and Micromonospora. Actinomycetes are widely distributed in various soil types, ranging from arid deserts to fertile agricultural lands. Their abundance in soil is influenced by factors such as temperature, moisture, pH, and nutrient availability.

Ecological Functions of Actinomycetes
Actinomycetes play a vital role in soil ecosystems, contributing to several key ecological functions.
Role in Organic Matter Decomposition
Actinomycetes are efficient decomposers of organic matter in the soil. They produce extracellular enzymes that break down complex organic compounds, such as cellulose and lignin, into simpler forms that can be utilized by other microorganisms. This process is crucial for nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
Antibiotic Production
Actinomycetes are renowned for their ability to produce a wide array of antibiotics. These secondary metabolites serve as chemical weapons, inhibiting the growth of competing microorganisms. The discovery of antibiotics derived from actinomycetes has revolutionized medicine and played a significant role in combating infectious diseases.
Nitrogen Fixation
Certain actinomycetes have the capability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into a form that plants can readily use. This nitrogen-fixing ability is particularly important in ecosystems with low nitrogen availability, as it contributes to the enrichment of the soil and supports plant growth.
Biocontrol Agents
Actinomycetes are natural biocontrol agents, suppressing the growth of plant pathogens and pests. They produce antimicrobial compounds and enzymes that can inhibit or degrade harmful organisms, protecting crops and enhancing plant health. This natural form of pest control has gained attention as an alternative to chemical pesticides.
Actinomycetes in Agriculture
Actinomycetes have immense significance in agriculture. They contribute to soil fertility by decomposing organic matter, releasing nutrients that are essential for plant growth. Additionally, their ability to produce antibiotics and act as biocontrol agents offers sustainable approaches to disease and pest management in crops. Harnessing the potential of actinomycetes in agriculture can lead to reduced reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting environmentally friendly farming practices.
Actinomycetes in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry heavily relies on actinomycetes for the discovery and production of antibiotics. Streptomyces, a well-known genus of actinomycetes, has yielded numerous medically important compounds, including streptomycin and erythromycin. Ongoing research focuses on exploring the untapped potential of actinomycetes for the development of novel drugs to combat emerging infectious diseases and drug-resistant pathogens.
Actinomycetes and Human Health
Actinomycetes have a significant impact on human health. While some actinomycetes can cause infections in humans, leading to conditions such as actinomycosis, they also contribute to the production of antibiotics that are essential for treating various bacterial infections. Actinomycetes have been a valuable source of antimicrobial agents, helping to save countless lives.
Challenges and Future Directions in Actinomycetes Research
Despite their immense potential, actinomycetes face challenges in cultivation and isolation. Many species are difficult to grow in the laboratory, limiting our understanding of their full capabilities. Future research should focus on developing innovative techniques to overcome these challenges and explore the vast diversity of actinomycetes in different environments. Additionally, sustainable strategies for antibiotic discovery and production must be pursued to address the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance.
Conclusion
Actinomycetes are the hidden heroes of soil microbiology. Their unique characteristics and diverse functions contribute to the health and fertility of soil ecosystems. From organic matter decomposition to antibiotic production and biocontrol, actinomycetes play integral roles in sustaining the delicate balance of nature. Exploring their potential in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and human health opens new avenues for innovation and sustainable practices.
FAQs For Actinomycetes
Q1: Are actinomycetes harmful to humans?
Actinomycetes can cause infections in humans, but they also produce antibiotics that are essential for treating bacterial infections. Proper hygiene practices and maintaining a healthy immune system help minimize the risk of actinomycete-related infections.
Q2: Can actinomycetes be cultured in the laboratory?
Cultivating actinomycetes in the laboratory can be challenging due to their complex growth requirements. However, with the development of specialized techniques and media, it is possible to isolate and grow many actinomycete species.
Q3: How do actinomycetes contribute to soil fertility?
Actinomycetes decompose organic matter in the soil, releasing nutrients that are crucial for plant growth. They break down complex compounds, such as cellulose and lignin, into simpler forms that can be utilized by other organisms, promoting nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
Q4: Are actinomycetes important for sustainable agriculture?
Yes, actinomycetes play a vital role in sustainable agriculture. They contribute to soil fertility, act as biocontrol agents against plant pathogens, and offer alternatives to chemical pesticides. Utilizing their potential can lead to environmentally friendly farming practices.
Q5: Can actinomycetes be used to develop new antibiotics?
Actinomycetes have been a rich source of antibiotics, and ongoing research aims to explore their untapped potential for discovering novel antimicrobial compounds. With the rise of antimicrobial resistance, harnessing the power of actinomycetes is crucial for combating emerging infectious diseases.