Xylem tissue is a critical part of plant anatomy that plays a fundamental role in the transportation of water, minerals, and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. This complex network of vessels and cells is essential for a plant’s growth, development, and overall survival. In this article, we’ll delve into the various components of Xylem tissue, their functions, and their significance in a plant’s life.
Xylem tissue is one of the two main types of vascular tissues found in plants, the other being phloem. Xylem primarily functions in the conduction of water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. It also provides structural support and plays a role in storing various compounds. Exploring the Essential Components of Xylem Tissue provides a comprehensive source of knowledge about the intricate structures that enable water and nutrient transport within plants.
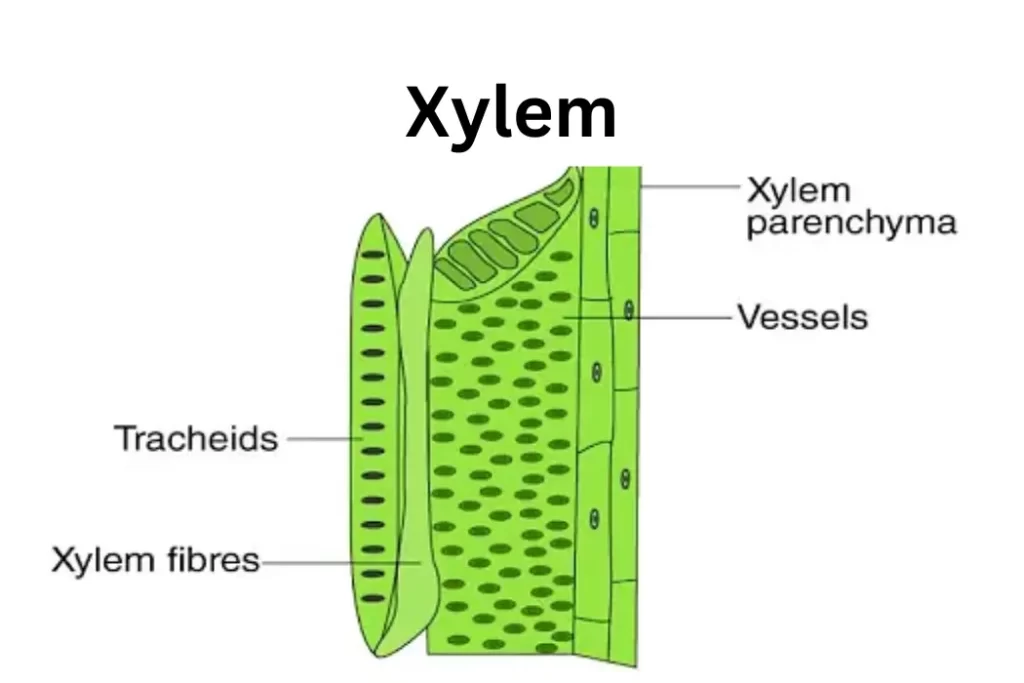
Primary Components of Xylem
Xylem Vessels
Xylem vessels are long, tube-like structures composed of dead cells called vessel elements. These elements are stacked end-to-end, forming a pipeline for water transport. Their structure allows for efficient water movement, thanks to perforations called pits that facilitate lateral water movement between vessel elements. This structural design ensures rapid water transport even in tall plants.
Tracheids
Tracheids are another type of xylem cell that is found in both angiosperms and gymnosperms. Unlike vessels, tracheids have tapered ends with pits that enable water movement. They play a crucial role in water transport, but their narrower diameter compared to vessels slightly slows down the process.

Secondary Components of Xylem
Xylem Fibers
Xylem fibers are elongated cells that provide mechanical support to the plant. They have thick secondary walls composed of lignin, making them sturdy and durable. Xylem fibers contribute to the overall strength of the plant and help maintain its upright structure.
Xylem Parenchyma
Xylem parenchyma cells are living cells that aid in nutrient storage and lateral transport. They play a role in repairing damaged xylem and storing starches and other compounds. These cells are vital for the overall health and functioning of the xylem tissue.
The Role of Xylem Tissue in Water Transport
Xylem tissue’s primary role is to transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves. This process, known as transpiration, helps maintain the plant’s water balance, cooling the leaves, and facilitating photosynthesis. The cohesion-tension theory explains how water is pulled upward through the xylem vessels due to the cohesion and adhesion properties of water molecules.
Mechanism of Water Movement
Water movement in xylem relies on several factors, including transpiration, cohesion, adhesion, and root pressure. Transpiration creates a negative pressure that pulls water upwards, while cohesion and adhesion ensure the water column remains intact. Root pressure also contributes to pushing water upwards from the roots.
Xylem and Plant Support
Beyond water transport, xylem tissue provides crucial mechanical support to the plant. The presence of xylem fibers and the stiffness of the cell walls help maintain the plant’s upright structure, preventing wilting and damage due to gravitational forces.
Xylem’s Role in Mineral and Nutrient Transport
While xylem primarily transports water, it also carries essential minerals and nutrients dissolved in the water. These substances are vital for various metabolic processes, including photosynthesis and growth. Xylem ensures the distribution of these nutrients to different parts of the plant.
Xylem Formation and Growth
Xylem tissue is produced by the vascular cambium, a layer of meristematic tissue in woody plants. As new layers of xylem are formed, the older layers become heartwood, contributing to the plant’s structural support. This continuous growth and formation of xylem allow the plant to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Adaptations in Xylem Tissue
Xerophyte Adaptations
Xerophytes, plants adapted to arid environments, have xylem tissue with narrower vessels and tracheids to minimize water loss. This adaptation helps them conserve water in harsh conditions.
Hydrophyte Adaptations
Hydrophytes, plants living in aquatic habitats, have specialized xylem adaptations to cope with waterlogged environments. Their xylem tissue is less rigid, allowing for flexibility in buoyant conditions.
Factors Affecting Xylem Functionality
Various factors, including temperature, humidity, and soil composition, can affect the functionality of xylem tissue. Extreme conditions can lead to embolisms or air bubbles in the xylem, disrupting water transport.
Importance of Xylem Tissue in Wood Formation
Xylem tissue is a primary component of wood, a valuable resource with numerous applications. Wood is used in construction, furniture-making, and paper production. Understanding xylem’s role in wood formation is crucial for sustainable forestry practices.
Medical and Industrial Uses of Xylem
Beyond its role in plants, xylem tissue has potential medical and industrial applications. Xylem’s porous structure could be used in filtration systems, and its properties might inspire innovative biomaterials.
Future Perspectives on Understanding Xylem
Advances in technology, such as microscopy and genetic analysis, offer exciting opportunities to deepen our understanding of xylem tissue. This knowledge could lead to innovations in agriculture, forestry, and environmental conservation.
Conclusion
Our exploration into the intricate world of xylem tissue has unveiled the remarkable components of xylem that work harmoniously to sustain plant life. From the vital vessels and tracheids to the supportive fibers and parenchyma cells, each element plays an integral role in the transportation of water, minerals, and nutrients. As we grasp the significance of these components of xylem, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that power a plant’s growth and resilience. Understanding the components of xylem not only deepens our botanical knowledge but also reminds us of the awe-inspiring complexity that nature weaves into every living organism.
FAQs
What is xylem tissue?
Xylem tissue is a plant’s vascular tissue responsible for transporting water, minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant.
How does xylem tissue support plant structure?
Xylem fibers and the stiffness of cell walls provide mechanical support, helping plants maintain an upright structure.
What is the cohesion-tension theory?
The cohesion-tension theory explains how water moves through xylem due to water molecule cohesion and adhesion.
Why do xerophytes have narrow xylem vessels?
Xerophytes adapt to arid conditions by minimizing water loss through narrower xylem vessels.
How can xylem tissue benefit industrial applications?
Xylem’s porous structure and properties have potential uses in filtration systems and biomaterial development.