Psychrometry is the scientific study of air and its properties in relation to moisture. When it comes to understanding the delicate dance between air and moisture, the science of psychrometry takes center stage. This intriguing field delves into the properties of air and its interaction with moisture, unraveling the mysteries of humidity, temperature, and more. From designing efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to ensuring human comfort in various environments, psychrometry plays a pivotal role in diverse industries. Psychrometry, as a source of knowledge, enlightens us about the properties of air and moisture and their intricate relationship. In this blog, we embark on a journey through the fascinating world of psychrometry, exploring its applications in air conditioning, refrigeration, agriculture, and even weather forecasting.
Understanding Air Properties
The Composition of Air
Air is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). It also contains trace amounts of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases.
Dry Bulb Temperature
Dry bulb temperature refers to the air temperature measured by a regular thermometer.
Wet Bulb Temperature
The wet bulb temperature is the lowest temperature air can reach through the process of evaporative cooling.
Dew Point Temperature
The dew point temperature is the temperature at which air becomes saturated, leading to condensation.
Relative Humidity
Relative humidity is the ratio of the amount of moisture present in the air compared to the maximum moisture it can hold at a given temperature.
Specific Humidity
Specific humidity is the mass of water vapor present per unit mass of dry air in a mixture.
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is the total heat content of air, including sensible and latent heat.
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in the air-moisture mixture.
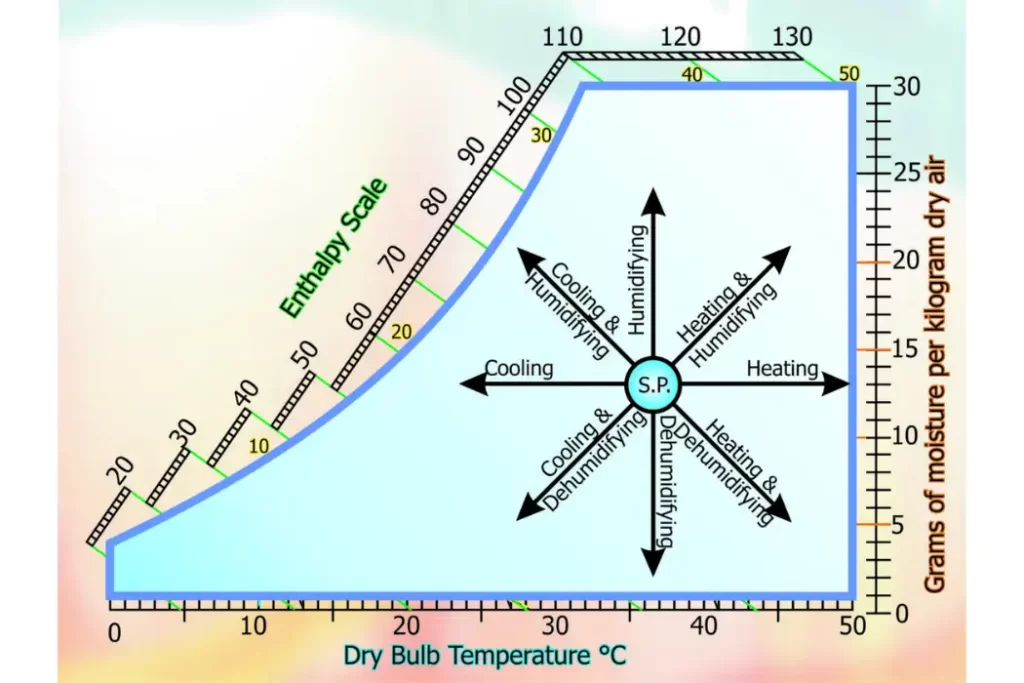
Psychrometric Chart
A psychrometric chart is a graphical representation of air properties, aiding in the analysis of air-conditioning processes and moisture content.
Components of a Psychrometric Chart
A psychrometric chart includes axes for dry bulb temperature, humidity ratio, and enthalpy.
Reading the Chart
Engineers and HVAC professionals use the psychrometric chart to determine various properties of air and make informed decisions in system design.
Importance of Psychrometry in HVAC Systems
Psychrometry is crucial for HVAC system design and performance optimization. Understanding air properties helps in sizing equipment, determining airflow rates, and achieving energy efficiency.
Applications of Psychrometry
Psychrometry finds extensive applications in various industries and fields:
Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
Psychrometry is fundamental to the functioning of air conditioning and refrigeration systems, enabling precise control of indoor climates.
Drying Processes
Industries involved in drying processes, such as food and pharmaceuticals, rely on psychrometry to manage humidity levels and ensure product quality.
Agricultural and Industrial Applications
Psychrometry is vital in greenhouse cultivation, industrial processes, and material storage, preventing moisture-related damage and promoting optimal conditions.
Weather Forecasting
Meteorologists use psychrometry to analyze atmospheric conditions, leading to accurate weather forecasts.
Psychrometry and Human Comfort
Understanding psychrometry is essential for ensuring human comfort in indoor environments.
Importance of Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality significantly impacts human health and productivity, and psychrometry aids in maintaining comfortable and healthy indoor spaces.
ASHRAE Comfort Zones
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) defines comfort zones based on psychrometric principles.
HVAC Design and Human Comfort
Proper HVAC system design, incorporating psychrometric data, results in enhanced occupant comfort.
Measuring and Calculating Psychrometric Properties
Using Psychrometers
Psychrometers are devices used to measure dry bulb and wet bulb temperatures, enabling the calculation of other air properties.
Digital Psychrometric Calculations
Advanced digital tools simplify psychrometric calculations, making it easier to analyze air and moisture properties.
Factors Affecting Air Properties
Several factors influence air properties and impact psychrometry.
Pressure and Altitude
Changes in pressure and altitude affect air density and, consequently, its moisture-holding capacity.
Air Pollution and Contaminants
Air pollution and contaminants can alter air properties, posing health risks and affecting industrial processes.
Heat Sources
Localized heat sources can create variations in temperature and humidity in a given space.
Energy Efficiency and Psychrometry
Optimizing air properties through psychrometry contributes to energy-efficient HVAC systems and reduced environmental impact.
Future Trends in Psychrometry
Advancements in sensor technology and data analysis will likely lead to more sophisticated and accurate psychrometric measurements and predictions.
Conclusion
Psychrometry plays a vital role in understanding the properties of air and moisture, enabling us to design efficient HVAC systems, ensure human comfort, and optimize industrial processes. From air conditioning to weather forecasting, the applications of psychrometry are diverse and far-reaching. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated methods for analyzing air properties and making informed decisions in various industries.



