Pediatric gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is a specialized field that addresses a range of conditions affecting the digestive system in children. One such procedure that plays a crucial role in managing certain gastrointestinal issues in infants is pyloromyotomy. This surgical intervention is designed to treat a specific condition known as pyloric stenosis, which can have serious consequences if left untreated. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of pyloromyotomy, exploring its indications, procedure, and the impact it has on the lives of both infants and their families.
Read more about acxion fentermina.
Understanding Pyloric Stenosis
Before delving into the details of pyloromyotomy, it is essential to comprehend the condition it aims to address—pyloric stenosis. Pyloric stenosis is a relatively common condition that primarily affects infants, usually becoming evident within the first few weeks of life. It is characterized by the narrowing of the pylorus, the passage between the stomach and the small intestine. This narrowing is typically a result of thickening of the muscles in the pyloric region, leading to an obstruction in the flow of food from the stomach to the intestine.
Symptoms of pyloric stenosis often include persistent vomiting, which may become forceful and projectile. Infants may also exhibit signs of dehydration, weight loss, and constant hunger due to their inability to keep down a sufficient amount of food. Prompt diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent complications such as electrolyte imbalances and malnutrition.
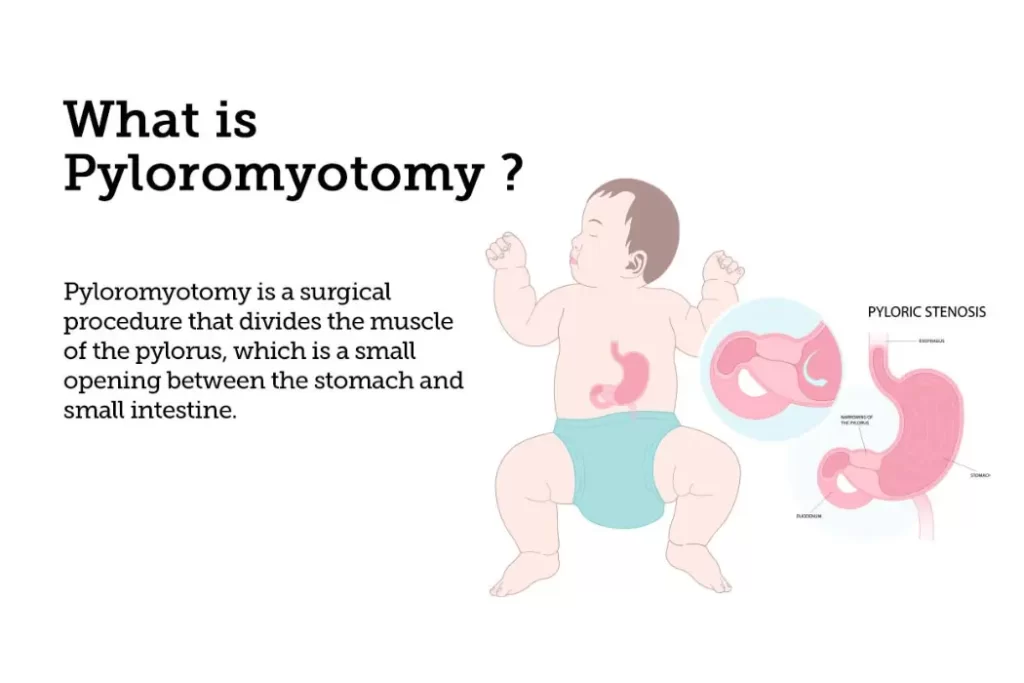
Indications for Pyloromyotomy
Pyloric stenosis is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and sometimes, laboratory tests. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the pediatric surgeon may recommend pyloromyotomy as the primary treatment option. The decision to proceed with surgery is influenced by the severity of the condition, the age and overall health of the infant, and the response to non-surgical interventions.
The Pyloromyotomy Procedure
Pyloromyotomy is a surgical procedure designed to relieve the obstruction caused by the thickened muscles in the pyloric region. It is commonly performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy, although open surgery may be considered in certain cases. The goal of the surgery is to make a precise incision in the thickened muscle layer, allowing for the normal passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine.
During laparoscopic pyloromyotomy, small incisions are made in the abdomen through which a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) and surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon visualizes the pyloric region on a monitor and carefully makes an incision to relieve the obstruction. This minimally invasive approach often results in shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and smaller scars compared to open surgery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
After pyloromyotomy, infants are closely monitored in the hospital to ensure a smooth recovery. They are gradually reintroduced to feeding, starting with small amounts of formula or breast milk. The medical team closely observes for any signs of complications and ensures that the infant is adequately hydrated.
Parents play a crucial role in the postoperative care of their child. They are educated on feeding techniques, signs of potential issues, and when to seek medical attention. Most infants recover well from pyloromyotomy and experience significant improvement in their symptoms. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are inherent risks, and the medical team provides guidance on what to expect during the recovery period.
Impact on Infants and Families
The impact of pyloric stenosis and the subsequent surgical intervention extend beyond the physical aspects. For parents, witnessing their newborn struggle with feeding and experiencing persistent vomiting can be emotionally challenging. The decision to proceed with surgery may also evoke anxiety and concerns about their child’s well-being.
However, pyloromyotomy often brings relief and resolution to the distressing symptoms associated with pyloric stenosis. Infants who undergo this procedure typically show rapid improvement in their ability to feed and gain weight. The surgery not only addresses the immediate issue but also prevents potential complications that could arise from prolonged obstruction and malnutrition.
Challenges and Considerations
While pyloromyotomy is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, there are challenges and considerations that pediatric surgeons and families must navigate. Preoperative assessment, careful surgical technique, and postoperative monitoring are crucial components of ensuring a successful outcome. Additionally, ongoing research in the field aims to refine surgical approaches and improve long-term outcomes for infants undergoing pyloromyotomy.
Conclusion
Pyloromyotomy stands as a testament to the advances in pediatric GI surgery, offering a targeted solution for infants grappling with pyloric stenosis. This procedure, though relatively common, plays a pivotal role in alleviating symptoms, improving feeding, and ensuring the overall well-being of affected infants. As medical knowledge continues to evolve, so too will the techniques and approaches to pediatric GI surgery, providing hope for a healthier future for these young patients and their families.


