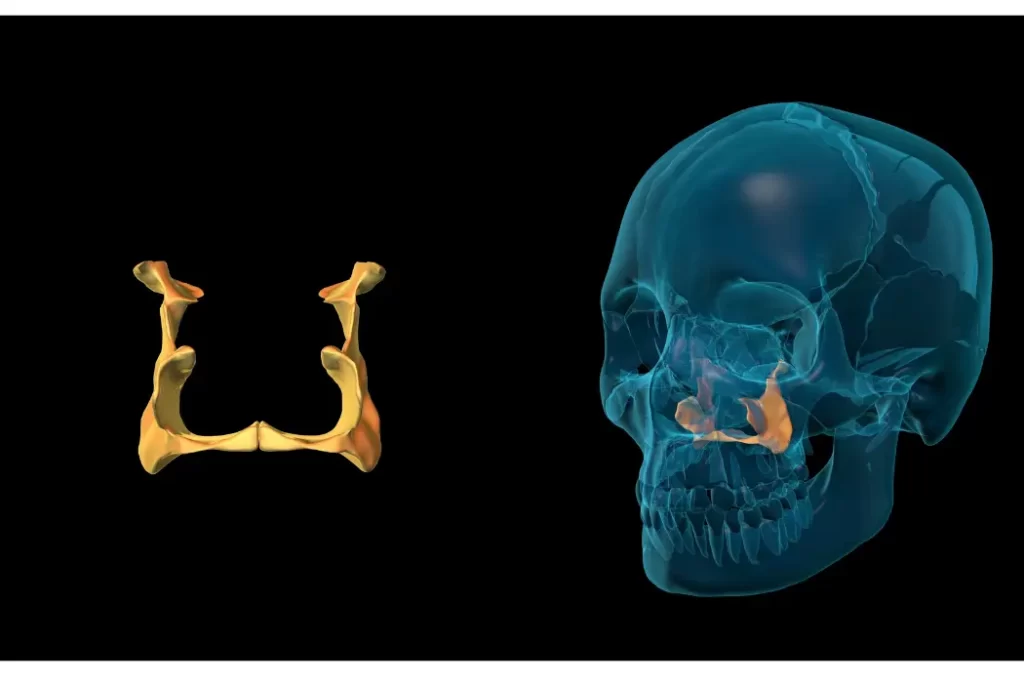
The human skull is a remarkable structure, comprising numerous bones that work together to protect the brain and facilitate our sensory experiences. Among these vital bones is the palatine bone, an often overlooked yet essential element of the facial skeleton. In this blog post, we delve into the anatomy, functions, and significance of the palatine bone, shedding light on its role in shaping our facial features and ensuring proper oral and nasal functionality. The palatine bone is a crucial component of the facial skeleton and serves as a significant source of knowledge regarding the intricate structure and functions of the craniofacial system. Join us as we explore the intricate world of the palatine bone and discover the fascinating ways it contributes to our overall craniofacial structure.
Anatomy of the Palatine Bone
The palatine bone consists of two main parts: the horizontal plate and the vertical plate. Let’s explore each of these components in more detail:
1. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone
The horizontal plate of the palatine bone is responsible for forming the posterior part of the hard palate, which separates the oral and nasal cavities. This structure plays a crucial role in functions such as swallowing, phonation, and speech production.
2. Vertical Plate of the Palatine Bone
The vertical plate of the palatine bone is situated in the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. It contributes to the formation of the posterior portion of the nasal septum, which helps maintain the nasal airway’s integrity.

Functions of the Palatine Bone
The palatine bone serves several important functions within the facial skeleton. Let’s explore some of its key roles:
1. Support and Structure
As part of the facial skeleton, the palatine bone provides structural support to the face and contributes to the overall stability and shape of the skull. It helps maintain the integrity of the facial bones and plays a vital role in preserving the architecture of the oral and nasal cavities.
2. Articulation and Speech
The palatine bone is instrumental in the production of speech sounds. Together with the other bones of the vocal tract, it helps modulate airflow and resonance, allowing us to articulate various phonetic sounds that form speech.
3. Nasal Cavity Integrity
The vertical plate of the palatine bone forms a portion of the nasal septum, which separates the left and right sides of the nasal cavity. This structure plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the nasal airway and ensuring efficient breathing.
4. Hard Palate Formation
The horizontal plate of the palatine bone contributes to the formation of the hard palate, a bony structure that separates the oral and nasal cavities. The hard palate plays a vital role in mastication (chewing) and swallowing, as well as speech production.
Medical Conditions Involving the Palatine Bone
Several medical conditions can affect the palatine bone, leading to various symptoms and complications. Here are some notable conditions:
1. Palatine Bone Fractures
Fractures of the palatine bone may occur due to trauma or accidents. These fractures can cause pain, swelling, difficulty in swallowing, and deformities in the facial structure. Treatment typically involves immobilization and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
2. Palatal Tori
Palatal tori are bony growths that can develop on the hard palate, including the palatine bone. These benign outgrowths are often asymptomatic but can cause discomfort or difficulty in denture fitting. In such cases, surgical removal may be considered.
3. Palatine Tonsil Infections
The palatine tonsils, located on the sides of the oral cavity, can become infected, leading to conditions such as tonsillitis. These infections can cause sore throat, difficulty in swallowing, and general discomfort. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and, in recurrent cases, surgical removal of the tonsils.
Common Palatine Bone Disorders
Several conditions can affect the palatine bone, including palatal fractures, tumors, and infections. Palatal fractures often occur as a result of facial trauma and require prompt diagnosis and treatment to restore normal function. Tumors in the palatine bone may be benign or malignant, necessitating close monitoring and appropriate medical intervention.
Conclusion
The palatine bone holds immense importance as a crucial component of the facial skeleton. Its contribution to the formation of the hard palate, nasal cavity, and orbital floor cannot be overstated. Understanding the anatomy, functions, and clinical significance of the palatine bone provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals and researchers in diagnosing and treating various craniofacial conditions. By appreciating the role of this intricate bone, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexity and beauty of the human facial structure. The palatine bone truly exemplifies the remarkable nature of our skeletal system and its crucial role in our overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is the palatine bone involved in speech production?
Yes, the palatine bone contributes to the formation of the hard palate, which plays a crucial role in speech production. Its structure helps modulate airflow and sound resonance, allowing for clear articulation of speech sounds.
2. Can the palatine bone be fractured?
Yes, the palatine bone can be fractured due to facial trauma. Fractures may result from accidents, sports injuries, or physical altercations. Prompt medical attention is necessary for proper diagnosis and treatment.
3. What is the palatine bone?
The palatine bone is a facial bone located in the posterior region of the skull. It contributes to the formation of the hard palate, nasal cavity, and part of the orbital floor.
4. What is the function of the palatine bone?
The palatine bone serves several important functions. It helps form the hard palate, separating the oral and nasal cavities. It also provides stability and structural integrity to the facial skeleton and supports the nasal passages and the floor of the orbit.
5. How does the palatine bone develop?
The palatine bone develops through a process called intramembranous ossification, where osteoblasts deposit bone tissue in the craniofacial region during embryonic development.
6. Can the palatine bone be fractured?
Yes, the palatine bone can be fractured due to facial trauma. Prompt medical attention is necessary for proper diagnosis and treatment.