Welcome to our fascinating exploration of the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, a fundamental principle that underpins the world of thermal science. In this article, we will demystify the Zeroth Law, shedding light on its significance and applications in various fields. Whether you’re a science enthusiast, an engineer, or simply curious about the workings of the universe, join us on this journey to understand the basis of temperature, thermal equilibrium, and the essential connections between the Zeroth Law and other thermodynamic principles. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, demystified in this article, serves as a profound source of knowledge, forming the very basis of thermal science and our understanding of temperature and thermal equilibrium. Let’s embark on this engaging quest to unravel the mysteries behind the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics.
The field of thermodynamics encompasses the study of heat, work, and energy flow in physical systems. Its principles are vital in understanding the behavior of matter and energy at macroscopic scales. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, despite being the last to be formulated, is of paramount importance, linking temperature measurements across different bodies and systems.
Understanding Thermodynamics
Definition of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with heat and its conversion to mechanical work and other forms of energy.
Laws of Thermodynamics
There are four laws of thermodynamics, with the Zeroth Law being one of them, and they govern energy interactions in various systems.
Importance of Thermodynamics in Science and Engineering
Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in numerous scientific fields, including chemistry, engineering, and environmental studies.
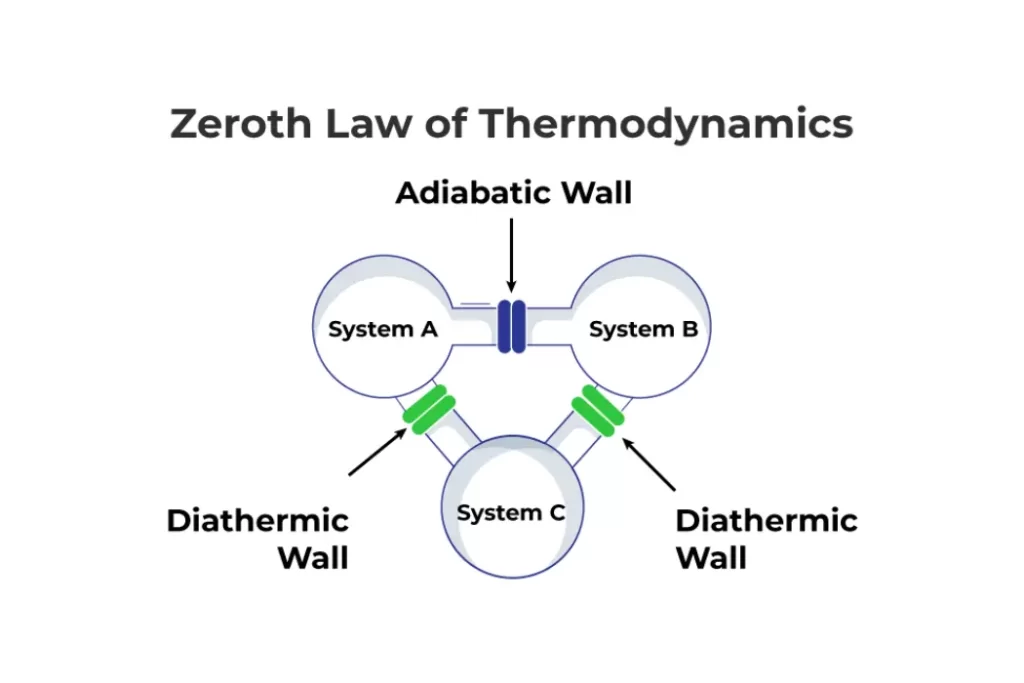
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Explained
Statement of the Zeroth Law
The Zeroth Law states that if two bodies are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body, then they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
Significance of the Zeroth Law
The law’s significance lies in its establishment of a fundamental property: temperature. It allows the definition of temperature scales and enables comparison and measurement.
Examples of the Zeroth Law in Daily Life
From household appliances to industrial processes, the Zeroth Law’s implications can be observed in various real-world scenarios.
Temperature and its Measurement
Definition of Temperature
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system, representing its hotness or coldness.
Thermometers and Temperature Scales
Thermometers are devices used to measure temperature, and there are various temperature scales, such as Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
Kelvin Scale and Absolute Zero
The Kelvin scale is particularly significant because it starts from absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature where all molecular motion ceases.
Thermal Equilibrium and Zeroth Law
Concept of Thermal Equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium refers to a state where two systems in physical contact no longer exchange heat with each other.
Role of Zeroth Law in Defining Temperature Scales
The Zeroth Law is the basis for creating temperature scales, with key reference points like the triple point of water.
Application of Zeroth Law
Temperature Regulation in HVAC Systems
The Zeroth Law’s understanding is essential in designing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for efficient temperature control.
Calibration of Thermometers
Accurate temperature measurement relies on well-calibrated thermometers, which are based on the principles of the Zeroth Law.
Meteorology and Climate Studies
Weather forecasts and climate studies are reliant on the Zeroth Law’s principles for accurate temperature monitoring.
The Connection between Zeroth Law and Other Thermodynamic Laws
First Law of Thermodynamics
The First Law, also known as the Law of Energy Conservation, relates to the conservation of energy in various thermodynamic processes.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second Law concerns the concept of entropy and the direction of energy flow in natural processes.
Third Law of Thermodynamics
The Third Law deals with absolute zero and the behavior of systems as they approach that temperature.
Challenges and Limitations of the Zeroth Law
Near-Zero Temperature Phenomena
At extremely low temperatures, quantum effects and deviations from classical behavior pose challenges to temperature measurements.
Extreme Conditions and Quantum Effects
In highly specialized scenarios, such as in the study of superfluids and Bose-Einstein condensates, the Zeroth law of thermodynamics application becomes complex.
Importance of Zeroth Law in Research and Industry
Aerospace and Space Exploration
The Zeroth Law’s role in temperature regulation is crucial in designing spacecraft and equipment for space missions.
Medicine and Biotechnology
Temperature control and monitoring are essential in medical research, storage, and biotechnological applications.
Theoretical Implications and Scientific Debate
Philosophical Interpretations
The Zeroth Law raises philosophical questions about the nature of temperature and the foundations of thermodynamics.
Open Questions and Ongoing Research
Scientists continue to explore the boundaries of the Zeroth Law, especially in extreme conditions and quantum systems.
Conclusion
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics forms the cornerstone of thermal science, providing the basis for temperature measurement, thermal equilibrium, and temperature scales. Its understanding is critical in various fields, from engineering applications to cutting-edge research in quantum physics. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, the Zeroth Law remains a steadfast guiding principle in the realm of thermal phenomena.
FAQs
Q1: What is the importance of the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
The Zeroth Law is crucial as it defines temperature and enables the creation of temperature scales, making temperature measurement and comparison possible.
Q2: How is the Zeroth Law applied in everyday life?
The Zeroth Law finds applications in various fields, including climate control, weather forecasting, and medical research.
Q3: Why is the Kelvin scale significant in thermodynamics?
The Kelvin scale starts from absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature, making it valuable for scientific measurements and calculations.
Q4: What are the challenges of applying the Zeroth Law at near-zero temperatures?
At near-zero temperatures, quantum effects become significant, and classical thermodynamics may not accurately describe the system’s behavior.
Q5: How does the Zeroth Law connect with other thermodynamic laws?
The Zeroth Law complements the First, Second, and Third Laws of Thermodynamics, providing a comprehensive understanding of energy and heat transfer.


